2025 IPv4 Adoption Targets
China’s push for IPv6 adoption—once a high-speed priority for Beijing—has encountered a slower trajectory, despite notable advancements. As of May 2024, the country reported 794 million active IPv6 users, with 64.56% of mobile traffic and 21.21% of fixed network traffic running on the protocol, according to data from the third China IPv6 Innovation and Development Conference. While these numbers reflect steady progress, they also highlight a decelerating growth curve compared to earlier years.
China’s progress toward its 2025 IPv6 adoption targets—800 million users, 70% of mobile traffic, and surpassing 15% fixed network traffic—is within reach. However, the moderate increase from May 2023’s 763 million users signals the need for renewed efforts to maintain momentum. Recognizing this, Beijing has introduced measures to accelerate adoption. One key policy mandates IPv6 compatibility for all new Wi-Fi routers sold in the country. Additionally, eight major cities, including Shanghai and Shenzhen, are set to pilot IPv6 programs targeting consumers, government agencies, and data centers. These urban hubs, home to over 110 million residents, are expected to play a pivotal role in boosting IPv6 penetration.
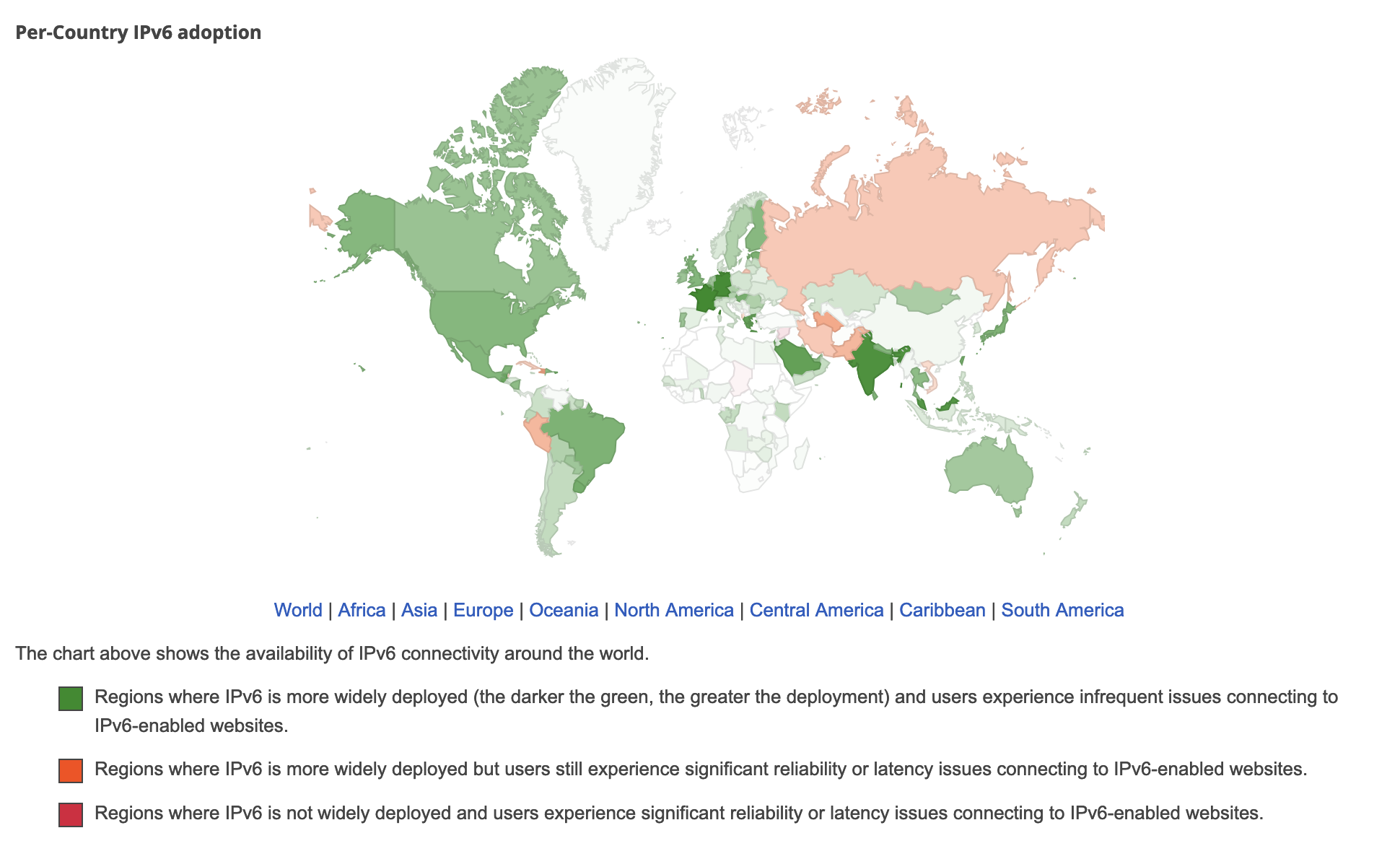
Global IPv6 Adoption, from Google’s IPv6 statistics
China’s emphasis on IPv6 adoption underscores its commitment to building a scalable, future-proof internet infrastructure. This is crucial as the country seeks to solidify its position in the digital age. However, it continues to lag behind global leaders such as India, Malaysia, and Germany. According to Akamai, China ranks 61st globally for IPv6 adoption, with a rate of just 22.2%. Similarly, APNIC reports a network readiness rate of 36.71%, far behind India’s 79.85%. With only one IPv4 address per 245 people, the need for a transition to IPv6 is more pressing than ever.
Advantages of IPv6 Adoption
IPv6 offers critical advantages, including improved network performance, enhanced manageability, and greater visibility—all essential for advancing China’s economic objectives and maintaining its tightly controlled internet ecosystem. The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) has been a key driver in this transition, issuing a directive to phase out IPv4-based Network Address Translation (NAT) systems in favor of IPv6. This “Network De-NAT” initiative reflects Beijing’s ambition to lead global IPv6 adoption efforts.
Challenges and the Path Ahead
While China’s strong policy support and infrastructure investments are driving progress, challenges remain. Achieving widespread adoption will require overcoming technical hurdles, ensuring interoperability, and fostering greater awareness among consumers and enterprises. The country’s success in meeting these challenges will determine its ability to close the gap with global frontrunners and fully realize the benefits of IPv6.
Conclusion
With ambitious targets, government backing, and strategic initiatives in place, China is doubling down on IPv6 to support its digital transformation. The coming years will be critical as the nation works to accelerate adoption and establish itself as a leader in next-generation internet technology.
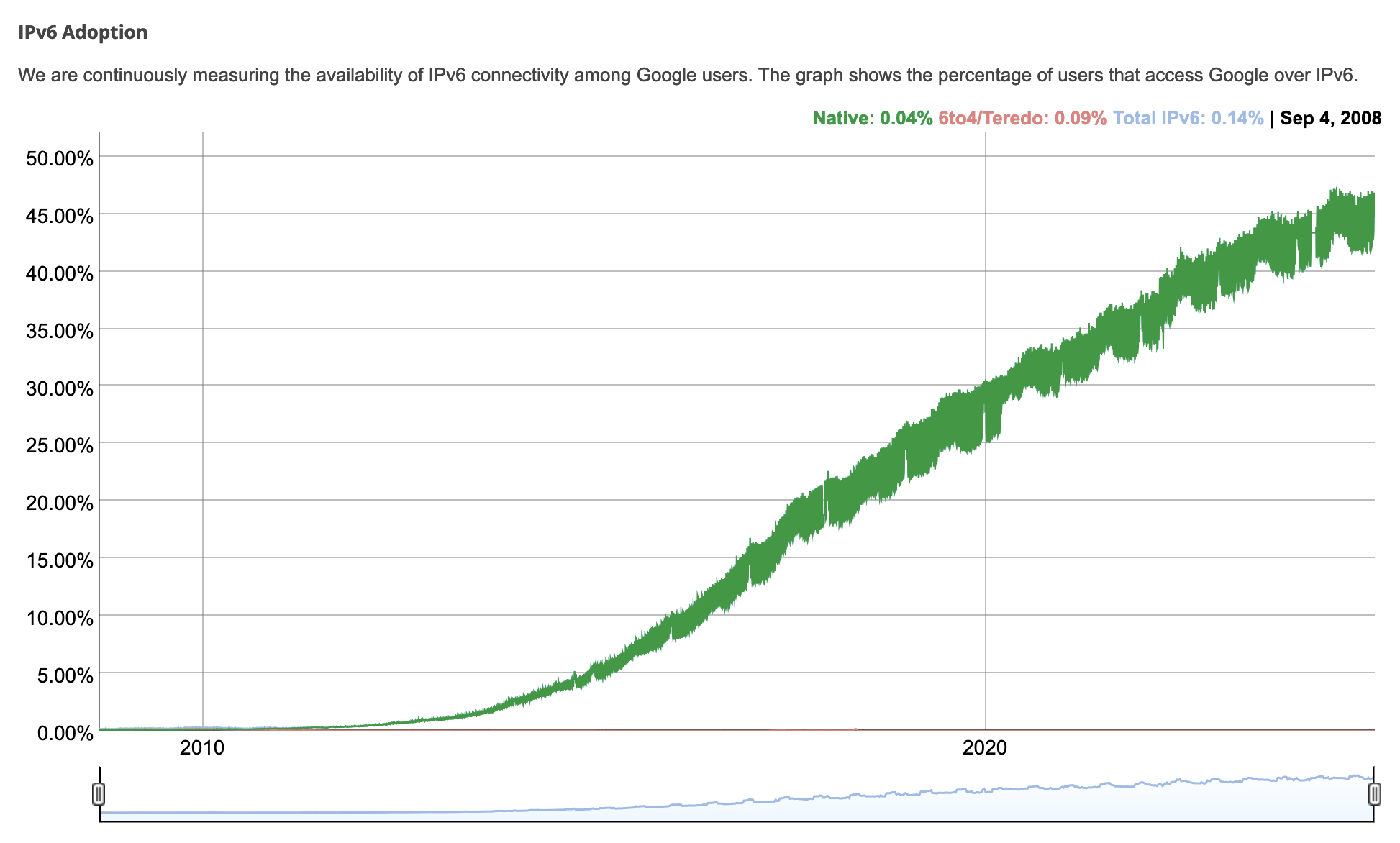
IPv6 adoption over time, from Google’s IPv6 statistics
◼️