05 April 2025 | IPv4 Blog , Knowledge Hub
Dealing with the Shortage of IPv4 Addresses
As the internet transitions from IPv4 to IPv6, network operators face the challenge of maintaining seamless connectivity. Two key technologies aiding this transition are MAP-T (Mapping of Address and Port with Translation) and CGNAT (Carrier-Grade Network Address Translation). While both help extend IPv4 functionality, they operate differently and have distinct advantages. Understanding their differences is crucial for making the right choice for your network infrastructure.
IPv4 has been the backbone of internet connectivity for decades, but the rapid expansion of online devices has led to IPv4 address exhaustion. At one time, 4.3 billion addresses seemed like plenty, but in today’s hyper-connected world, this number has proven insufficient. Operators now face a tough decision:
- Purchase additional IPv4 addresses, though at a rising cost of $30 to $40 per address or more, this is a costly short-term fix.
- Migrate entirely to IPv6, a long-term necessity, but one that requires substantial planning and infrastructure upgrades.
- Extend existing IPv4 investments while transitioning to IPv6, an approach that balances cost and future-readiness.
MAP-T and CGNAT are two critical technologies that help operators manage this transition effectively.
What is CGNAT? (Carrier-Grade NAT)
CGNAT is a stateful network address translation solution that enables multiple users to share a single public IPv4 address. It was designed to alleviate IPv4 exhaustion by mapping multiple private IP addresses to a limited number of public addresses. However, because CGNAT tracks the state of every single lease, session, and IP assignment, it has significant hardware requirements.
IPv4 to IPv6 Mapping using CGNAT
Key Benefits of CGNAT:
- Extends IPv4 Lifespan – Helps ISPs conserve IPv4 addresses by allowing multiple users to share a single public IP address.
- Delays Costly IPv6 Transition – Provides a temporary solution for ISPs and businesses that haven’t fully migrated to IPv6.
- Enhances Network Management – Allows ISPs to control and optimize IP address allocation efficiently.
- Supports Large-Scale NAT – Enables high-volume address translation for large networks, reducing the need for extensive IP renumbering.
Challenges of CGNAT:
- Hardware-intensive – Requires significant CPU, database, and memory resources.
- Higher latency – Stateful NAT processing can slow down performance.
- Application issues – Some applications, such as VoIP and gaming, may not work properly due to NAT limitations.
- Security risks – CGNAT creates a single point of failure and increases exposure to DDoS attacks.
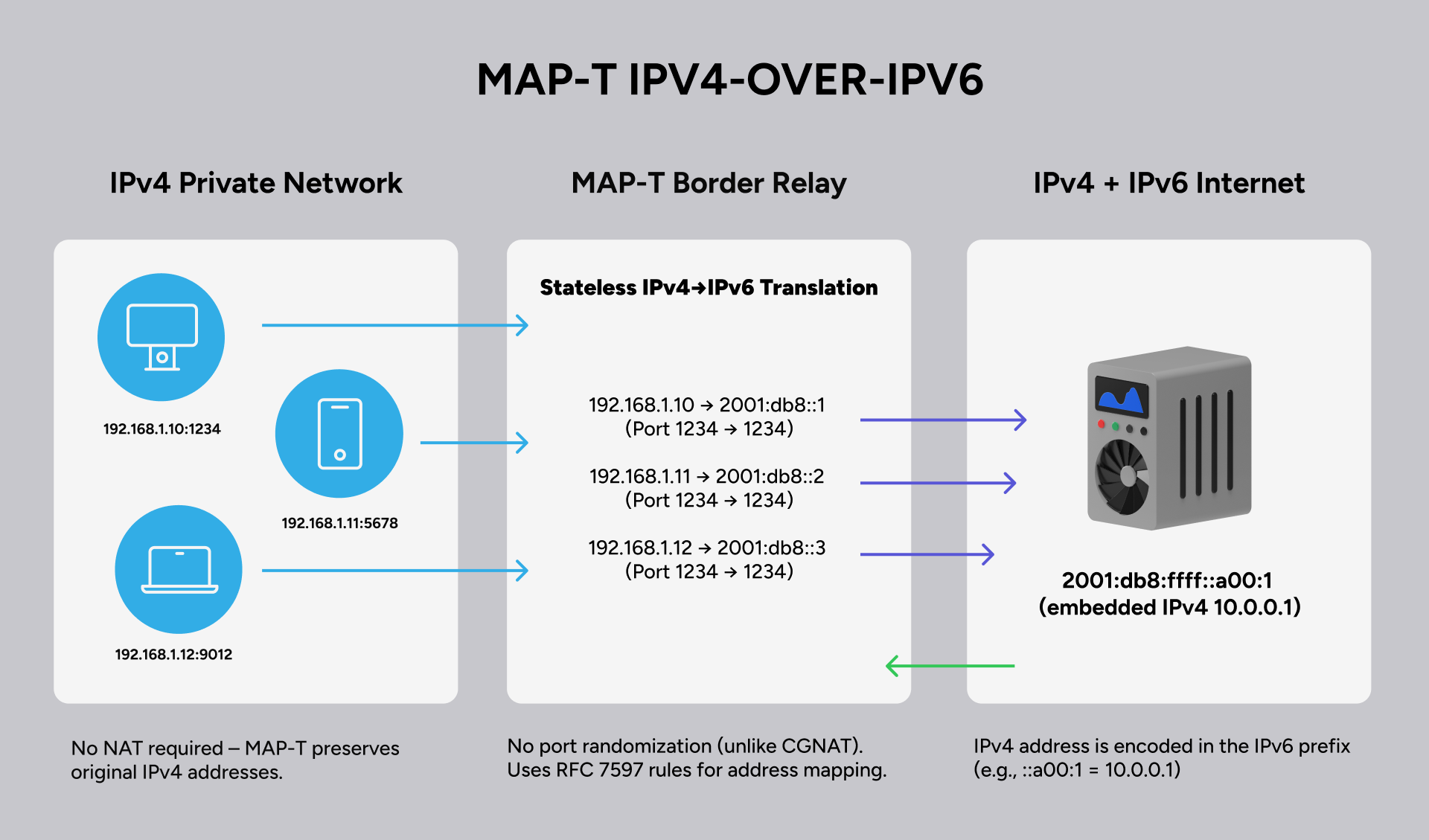
What is MAP-T? (Mapping of Address and Port with Translation
MAP-T is a stateless IPv4-to-IPv6 transition technology that enables IPv4 traffic to pass over an IPv6-only network. Unlike CGNAT, MAP-T does not require maintaining large translation tables, making it a more scalable and efficient solution for network operators.
Key Benefits of MAP-T:
- Stateless operation – No session tracking, reducing hardware costs and improving performance.
- Lower latency – Direct IPv4-to-IPv6 mapping eliminates unnecessary processing overhead.
- More scalable – Allows operators to deploy IPv6 while still supporting IPv4 connectivity.
- Better security – Without a NAT table, there is a smaller attack surface for cyber threats.
Challenges of MAP-T:
- IPv6 Dependency – Requires a fully deployed IPv6 network, making it difficult for ISPs still reliant on IPv4.
- Complex Deployment – Involves more intricate configuration and routing compared to traditional NAT solutions.
- Limited IPv4 Support – Some legacy IPv4 applications and services may not function properly without modifications.
- Troubleshooting Difficulties – Stateless mapping can make diagnosing connectivity issues more challenging compared to stateful NAT solutions like CGNAT.
MAP-T vs. CGNAT: Which One Should You Choose?
| Feature | MAP-T | CGNAT |
|---|---|---|
| Translation Type | Stateless | Stateful |
| IPv6 Readiness | Designed for IPv6 networks | Extends IPv4 lifespan |
| Performance | Lower latency, better scalability | Higher latency due to stateful processing |
| Hardware Requirements | Minimal | High |
| Security | No NAT table, reducing attack surface | Stateful NAT can be targeted for DDoS attacks |
| Application Compatibility | Works well with most applications | Can break certain applications like VoIP and gaming |
MAP-T is an ideal solution for ISPs looking to scale IPv6 while maintaining IPv4 support. Meanwhile, CGNAT is a short-term fix for managing IPv4 exhaustion but comes with higher costs and performance trade-offs.
Summary:
The transition from IPv4 to IPv6 presents a critical challenge for network operators as IPv4 addresses become increasingly exhausted. To manage this shift, technologies like MAP-T (Mapping of Address and Port with Translation) and CGNAT (Carrier-Grade Network Address Translation) provide key solutions. While CGNAT is designed to extend the life of IPv4, MAP-T offers a more scalable and efficient path for operators aiming to fully embrace IPv6. Both solutions have distinct benefits and challenges, and choosing the right approach depends on an operator’s specific needs, network infrastructure, and future-readiness.
How We Can Help:
Brander Group’s expertise in network infrastructure and transition strategies makes them well-equipped to guide businesses through the complexities of IPv4 exhaustion and the move to IPv6. Their special skills include:
- In-depth knowledge of MAP-T and CGNAT technologies: Brander Group understands the technical details and can help businesses implement the most suitable solution for their needs, whether it’s extending IPv4 or preparing for a complete IPv6 deployment.
- Customized infrastructure planning: We can assist in planning and deploying scalable network solutions, ensuring that businesses can maintain seamless connectivity during the transition without costly interruptions.
- Optimized performance and security: By leveraging their experience with both technologies, Brander Group ensures that the chosen solution minimizes latency and enhances network security, reducing the risk of attack and ensuring efficient operation.
- End-to-end transition support: From planning and deployment to troubleshooting and optimization, Brander Group provides comprehensive support throughout the entire IPv6 migration process.
Our expertise helps businesses navigate the intricacies of IPv4 to IPv6 migration, ensuring a smooth, cost-effective, and secure transition.
◼️