What Is Reverse DNS?
27 November 2025 | IPv4 Blog
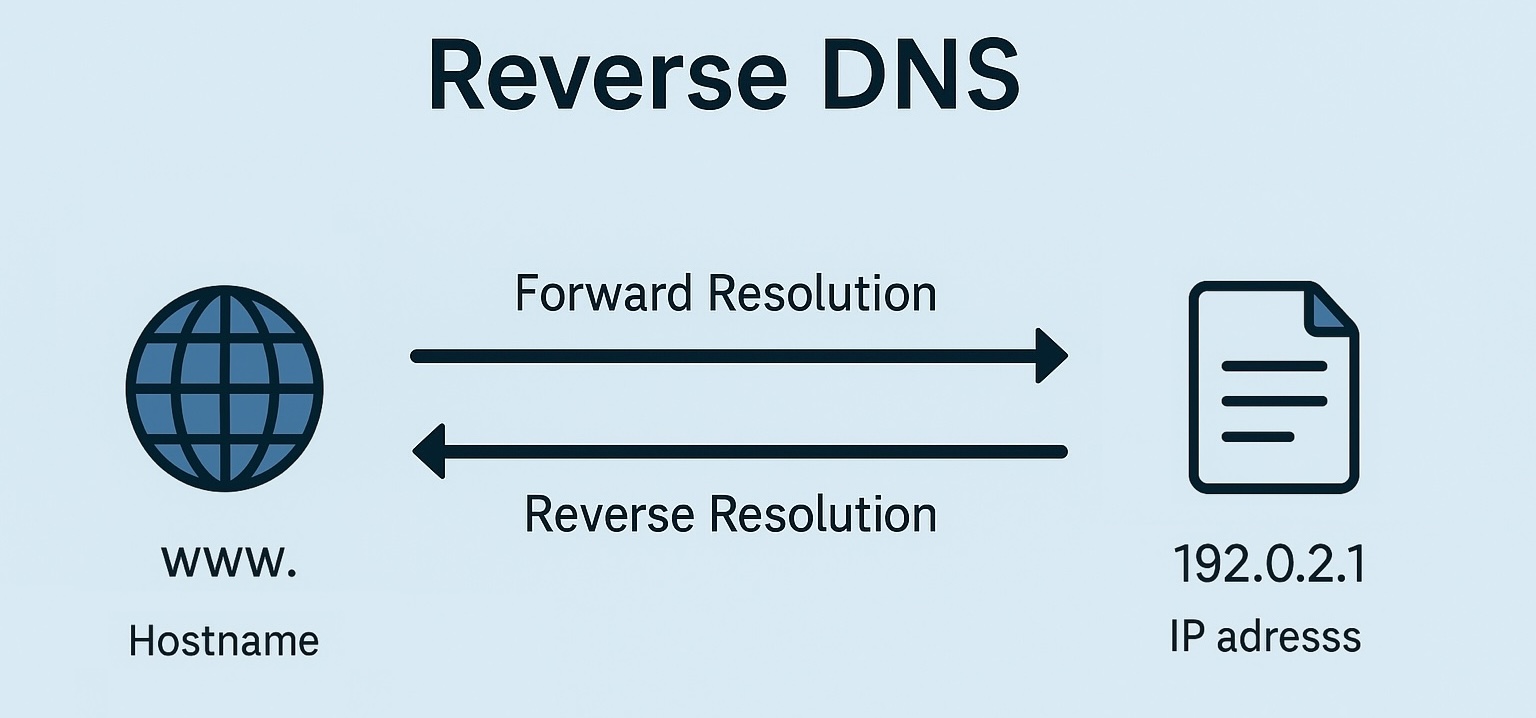
The Domain Name System (DNS) is best known for translating human-readable hostnames into IP addresses, a process called forward resolution. When a user enters a website address into a browser, DNS returns the IP address of the server hosting that site.
How rDNS Works
The reverse lookup system operates under two specialized DNS domains:
- in-addr.arpa for IPv4 addresses
- ip6.arpa for IPv6 addresses
Each IP address corresponds to a PTR record within one of these domains. The PTR record points the address back to a hostname. Maintaining accurate records is essential for proper reverse resolution.
ARIN requires organizations to maintain PTR records for address space registered to them in order to keep the global DNS infrastructure functioning reliably.
Why Reverse DNS Matters
Reverse resolution plays an important role in network operations, security, and trust. Common uses include:
- Network troubleshooting and diagnostics
- Identifying suspicious or generic hostnames tied to dynamically assigned IPs
- Email spam and phishing detection
- Traffic logging and analysis on web and application servers
Many mail servers and security platforms rely on properly configured rDNS as part of reputation and validation checks.
Managing Reverse DNS Delegations Through ARIN
ARIN provides tools that allow organizations to manage reverse DNS delegations for both IPv4 and IPv6 networks.
For IPv4, delegations are managed on bit boundaries such as /8, /16, and /24. IPv6 delegations are managed on nibble boundaries, meaning every four bits of the address.
ARIN supports CIDR-aligned IPv4 delegations of /24 and larger. Delegation size is determined by the CIDR blocks that make up an organization’s direct allocation.
Examples of IPv4 Delegation
An organization holding a /23 allocation will typically receive two /24 delegations, each of which can be assigned to different name servers.
By contrast, an organization with a /16 allocation receives a single delegation and manages reverse records for the entire block at that level.
How Delegations Are Modified
Organizations can manage rDNS information in two primary ways:
- ARIN Online: Suitable for managing smaller numbers of delegations
- RESTful Web Service: Designed for automated management at scale
Use of the RESTful service requires an API key issued by ARIN.
Who Can Manage rDNS?
Both direct and indirect resource holders may manage reverse DNS under certain conditions.
Organizations that receive address space directly from ARIN can manage their own delegations. Those receiving space from an ISP may share authority through SWIP, depending on how the space is reassigned or reallocated.
If address space is delegated from an ISP’s /16 or larger block without shared authority, DNS management remains with the ISP.
ISPs should promptly remove delegations when customers disconnect to ensure authority over reverse zones is properly revoked.
Securing Reverse DNS with DNSSEC
ARIN supports securing reverse DNS zones using Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC). DNSSEC protects DNS data by digitally signing records using cryptographic keys.
Once a zone is secured, organizations submit Delegation Signer (DS) records to ARIN to indicate that DNSSEC is enabled. DS records can be managed through ARIN Online or the RESTful provisioning system.
DNSSEC improves trust and integrity across reverse lookup infrastructure.
◼️




Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!